.NET Code Coverage in Azure DevOps and SonarCloud
Using SonarCloud to display code coverage with a .NET application managed with Azure DevOps
Sonar offer some really useful products for analysing the quality of your application’s source code. There’s a great mix of free and paid products, including SonarQube Cloud (formerly known as SonarCloud), SonarQube Server (for on-prem), and SonarQube for IDE (formerly SonarLint) static code analysers for IntelliJ, Visual Studio, VS Code and Eclipse.
I was looking to integrate an Azure DevOps project containing a .NET application with SonarQube Cloud, and in particular include code coverage data both for Azure Pipelines (so you can view the coverage in the pipeline run), but also in SonarQube Cloud.
This process is quite similar if you’re using the self-hosted SonarQube Server product, though note that there are different Azure Pipeline tasks provided by a different extension for SonarQube Server.
A sample project can be found at https://dev.azure.com/gardiner/SonarCloudDemo
Prerequisites
- You have a SonarQube Cloud account.
- You’ve configured it to be integrated with your Azure DevOps organisation.
- You’ve installed the SonarQube Cloud extension (or SonarQube Server extension if you’re using SonarQube Server)
- You’ve created a service connection in the Azure DevOps project pointing to SonarQube Cloud.
I’ve created a .NET solution which contains a simple ASP.NET web application and an xUnit test project.
By default, when you add a new xUnit test project, it includes a reference to the coverlet.collector NuGet package. This implements a ‘Data Collector’ for the VSTest platform. Normally you’d run this via:
dotnet test --collect:"XPlat Code Coverage"You would then end up with a TestResults subdirectory which contains a coverage.cobertura.xml file. But the problem here is that the xml file is one level deeper - VSTest creates GUID-named subdirectory under TestResults. So you will need to go searching for the file, there’s no way to ensure it gets created in a known location.
It turns out that’s a problem for Sonar, as the SonarCloudPrepare task needs to be told where the code coverage file is located, and unfortunately that property doesn’t support wildcards!
We can solve that problem by removing the reference to coverlet.collector, and instead adding a package reference to coverlet.msbuild.
dotnet remove package coverlet.collector
dotnet add package coverlet.msbuildTo collect code coverage information with this package, you run it like this:
dotnet test /p:CollectCoverage=trueBut more importantly, it supports additional parameters so we can now fix the location of output files. The CoverletOutput property lets us define the directory (relative to the test project) where output files will be written.
dotnet test /p:CollectCoverage=true /p:CoverletOutput='./results/coverage' /p:CoverletOutputFormat=coberturaNotice that I’ve not just set CoverletOutput to the directory (results), but also the first part of the coverage filename (coverage).
In the pipeline task, you can let SonarQube know where the file is by setting sonar.cs.opencover.reportsPaths like this:
- task: SonarCloudPrepare@3
inputs:
SonarQube: "SonarCloud"
organization: "gardiner"
scannerMode: "dotnet"
projectKey: "Gardiner_SonarCloudDemo"
projectName: "SonarCloudDemo"
extraProperties: |
sonar.cs.opencover.reportsPaths=$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Tests/results/coverage.opencover.xml
SonarQube and Azure Pipelines coverage
So now we’ve solved the problem of where the coverage file will be saved. Can we also deliver the coverage data to both SonarQube and Azure Pipelines?
Let’s review what we need to make that happen.
According to the docs for coverlet.msbuild, it supports generating the following formats:
- json (default)
- lcov
- opencover
- cobertura
- teamcity*
(The TeamCity format just generates special service messages in the standard output that TeamCity will recognise, it doesn’t create a file)
According to the docs for SonarCloud, it supports the following formats for .NET code coverage:
- Visual Studio Code Coverage
- dotnet-coverage Code Coverage
- dotCover
- OpenCover
- Coverlet (OpenCover format)
- Generic test data
The docs for the Azure Pipelines PublishCodeCoverageResults@2 task don’t actually mention which formats are supported (hopefully this will be fixed soon). But in the blog post that announced the availability of the v2 task the following formats were mentioned (including ones from the v1 task):
- Cobertura
- JaCoCo
- .coverage
- .covx
So unfortunately there isn’t a single format that all three components understand. Instead we will have to ask coverlet.msbuild to generate two output files - OpenCover for SonarQube, and Cobertura for Azure Pipelines.
We want to generate two outputs, but there is a known problem with trying to pass in parameters to dotnet test on Linux. The workaround is to set properties in the csproj file instead.
<PropertyGroup>
<CoverletOutputFormat>opencover,cobertura</CoverletOutputFormat>
</PropertyGroup> Our Azure Pipeline should look something like this:
steps:
- checkout: self
fetchDepth: 0
- task: SonarCloudPrepare@3
inputs:
SonarQube: "SonarCloud"
organization: "gardiner"
scannerMode: "dotnet"
projectKey: "Gardiner_SonarCloudDemo"
projectName: "SonarCloudDemo"
extraProperties: |
# Additional properties that will be passed to the scanner, put one key=value per line
# Disable Multi-Language analysis
sonar.scanner.scanAll=false
# Configure location of the OpenCover report
sonar.cs.opencover.reportsPaths=$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Tests/results/coverage.opencover.xml
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: build
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: test
projects: "Tests/Tests.csproj"
arguments: "/p:CollectCoverage=true /p:CoverletOutput=results/coverage"
- task: SonarCloudAnalyze@3
inputs:
jdkversion: "JAVA_HOME_17_X64"
- task: SonarCloudPublish@3
inputs:
pollingTimeoutSec: "300"
- task: PublishCodeCoverageResults@2
inputs:
summaryFileLocation: "$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Tests/results/coverage.cobertura.xml"
failIfCoverageEmpty: trueA few things to point out:
- We’re doing a full Git clone (not shallow) so that SonarQube can do a proper analysis. This avoids you seeing warnings like this:
- [INFO] SonarQube Cloud: Analysis succeeded with warning: Could not find ref ‘main’ in refs/heads, refs/remotes/upstream or refs/remotes/origin. You may see unexpected issues and changes. Please make sure to fetch this ref before pull request analysis.
- [INFO] SonarQube Cloud: Analysis succeeded with warning: Shallow clone detected during the analysis. Some files will miss SCM information. This will affect features like auto-assignment of issues. Please configure your build to disable shallow clone.
- Set
sonar.scanner.scanAll=falseto avoid this warning:- [INFO] SonarQube Cloud: Analysis succeeded with warning: Multi-Language analysis is enabled. If this was not intended and you have issues such as hitting your LOC limit or analyzing unwanted files, please set “/d:sonar.scanner.scanAll=false” in the begin step.
And now we can view our code coverage in SonarQube:
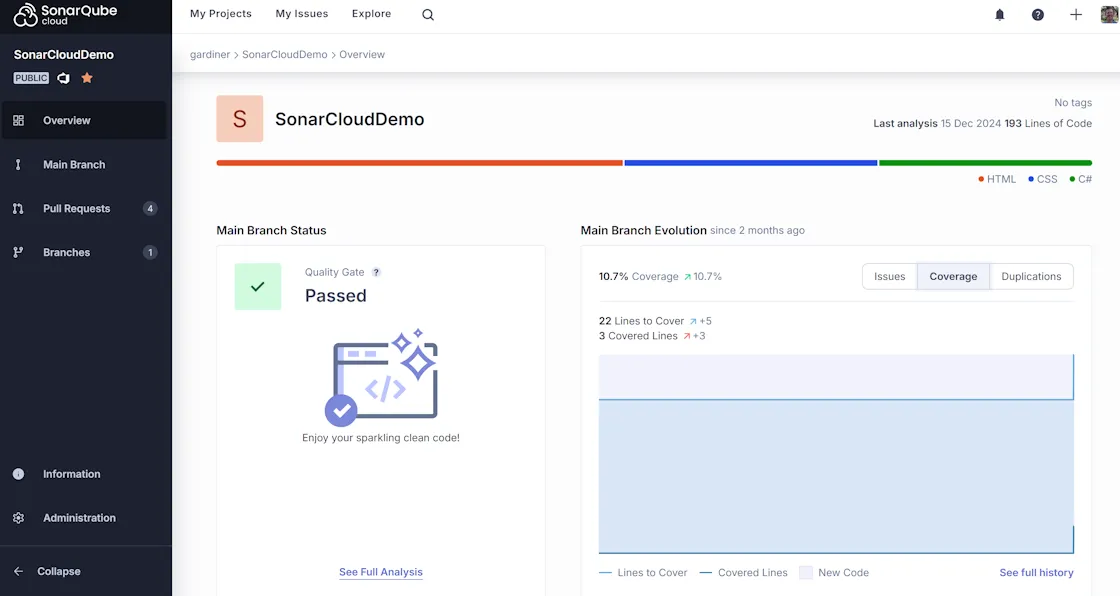
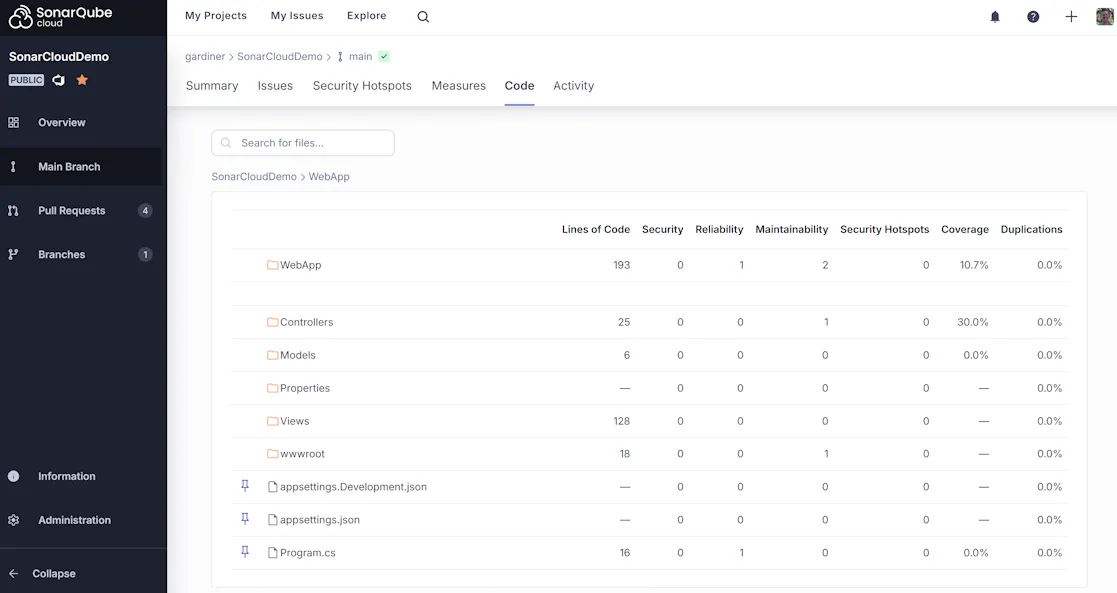 And in Azure Pipelines!
And in Azure Pipelines!
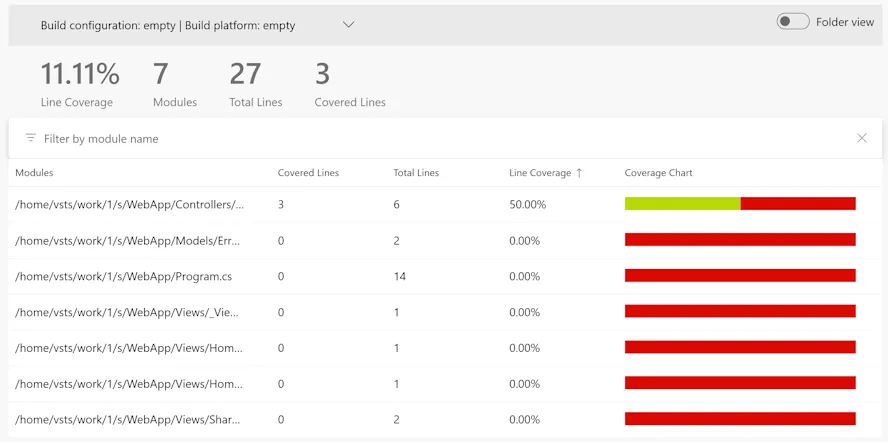
Check out the example project at https://dev.azure.com/gardiner/_git/SonarCloudDemo, and you can view the SonarQube analysis at https://sonarcloud.io/project/overview?id=Gardiner_SonarCloudDemo