-
Find where an object is unintentionally being converted to a string
I’ve been applying the Replace Primitive with Object pattern to a code base - changing what used to be strings into a custom type (which not only makes the code more readable, but now ensures through type safety that you can’t accidentally pass in any old random values to methods that used to just take strings.
The code has tests, and after applying the refactoring, I have a failing test - which hints that somewhere there’s an implicit conversion from the new strongly typed object back to a string. The test’s failing assertion says it received “MyNamespace.TypedThing” (which is what the default implementation of
ToString()returns), rather than the wrapped string value thatTypedThingencapsulates.My initial suspicion is that there’s probably code similar to this that’s causing the problem:
TypedThing thing = new TypedThing("thingy"); string s = $"{thing}";ReSharper has a cool utility - “Structural Search and Replace”. Unfortunately it doesn’t work for single expressions like
"{thing}".If I was cluey, I might be able to write a Roslyn tool to search the code and find instances like that, but that’s going to take a bit more effort than I want.
What about this: temporarily override the
ToString()method on my custom type, and make it throw an exception!It’s a bit of a sledgehammer, but it worked!
As it turns out my suspicion was not quite correct. The offending code was actually assigning the custom type to an
Objecttype (which explains the lack of compiler type warnings), which later on must be converted to a string.Now that I could see an example, I could use ReSharper’s SSR to confirm that was the only instance of that kind of assignment (SSR can be used as I’m searching for an assignment statement, not just a single expression). Just for good measure, I’ll also re-run the entire test suite to make sure there aren’t any other similar problems still hiding.
-
Choco list -localonly (Feb 2019 Edition)
What software / applications am I using on my laptop (February 2019 Edition) according to Chocolatey? Here’s an edited list of the output from
choco list -localonly:| Package | Version | | Comments | | — | — | — | — | | 7zip | 18.6 | | | 7zip.commandline | 16.02.0.20170209 | | | audacity | 2.3.0 | Audio editor | | becyicongrabber | 2.30.0.20161027 | Icon extractor (for creating Chocolatey packages) | | beyondcompare | 4.2.9.23626 | My favourite file comparison tool | | beyondcompare-integration | 1.0.1 | Configure Beyond Compare for TortoiseGit/Svn | | dellcommandupdate-uwp | 3.0.0 | Dell’s driver update app | | dns-benchmark | 1.3.6668.0 | Useful DNS checker | | docker-for-windows | 99.0.0.0 | | | dotnetdeveloperbundle | 2.3.0.2563 | RedGate’s .NET tools | | dropbox | 41.4.80 | | | fiddler | 5.0.20182.28034 | | | FiraCode | 1.206 | Nice developer font | | Firefox | 57.0.4 | | | git | 2.20.1 | | | GoogleChrome | 63.0.3239.132 | | | iTunes | 12.9.3.3 | | | keepass | 2.41 | Password manager | | microsoft-teams | 1.1.00.2251 | | | mousewithoutborders | 2.1.8.105 | Share mouse across laptop and desktop PCs | | msbuild-structured-log-viewer | 2.0.61 | | | nodejs | 11.9.0 | | | notepadplusplus | 7.6.3 | Using this less now compared to VS Code | | nuget.commandline | 4.9.2 | | | obs-studio | 22.0.2 | Video / screen recording | | OctopusTools | 5.2.0 | | | Office365ProPlus | 2016.20170321 | | | paint.net | 4.1.5 | | | PDFXchangeEditor | 7.0.328.2 | My favourite | | Pester | 4.4.1 | PowerShell unit tests | | pingplotter | 5.8.10 | Useful visual ping network status | | powershell-core | 6.1.2 | | | procmon | 3.50 | SysInternals Process Monitor | | resharper-clt.portable | 2018.3.2 | ReSharper’s free command-line tools | | resharper-ultimate-all | 2018.3.2 | | | screentogif | 2.16 | Handy screen recorder | | skype | 8.38.0.138 | | | snagit | 2019.1.0 | Screen grabber | | sql-server-2017 | 14.0.1000 | | | sql-server-management-studio | 14.0.17289.1 | | | tailblazer | 0.9.0.536 | Text/log file viewer | | tortoisegit | 2.7.0.0 | | | tortoisesvn | 1.11.1.28492 | | | ubiquiti-unifi-controller | 5.9.29 | Software for managing UniFi wireless access points | | vagrant | 2.2.3 | Manage virtual machines | | visualstudio2017enterprise | 15.2.26430.20170605 | | | visualstudiocode | 1.19.3 | | | vsts-cli | 0.1.4.20190126 | Command line tool for managing Azure DevOps | | vswhere | 2.6.7 | | | wifiinfoview | 2.42 | | | windirstat | 1.1.2.20161210 | Where’s all that disk space being used? | | wireshark | 2.6.5 | | | x-lite | 5.4.0.94388 | VoIP client | | yarn | 1.13.0 | | | zoomit | 4.50.0.20160210 | Great for presentations |
This is also a good basis for refreshing my Boxstarter scripts.
-
TimeoutException (aka Tour Down Under 2019 and a week off)
Back at work for a couple of weeks of 2019 and I don’t want to rush things too much, so I organised to take an extra week off after this year’s Tour Down Under bike ride.
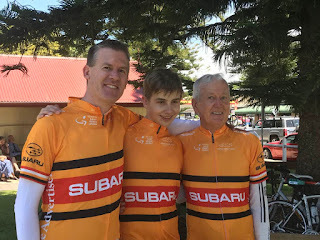
Last year’s community ride (the ‘Challenge Tour’) had to be cancelled due to hot weather. We’ve had our share of hot weather again this year, but fortunately Saturday (previously Friday) turned out to be ideal. This year I rode with my dad and my son - 3 generations of Gardiners! Very proud of my son, who completed the 100km distance (his furthest ridden) plus (impressing a lot of our fellow riders) he did it on a mountain bike (as he doesn’t have a road bike).
I didn’t need the week off to recuperate from the ride - instead I was catching up with relatives visiting Adelaide! It was great to see them lots of time during the week.
We all just made it through the 46.6°C record maximum temperature for Adelaide on Thursday (that was a really, really hot day).
<a href=/assets/2019/01/20190125_002103543_ios.jpg imageanchor="1" style="margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"><img alt="A ropes course" border="0" data-original-height="907" data-original-width="1210" height="239" src=/assets/2019/01/2_20190125_002103543_ios.jpg title="" width="320"></a> I watched as my son and his cousin did the ropes course at West Beach <a href=/assets/2019/01/20190119_025247040_ios.jpg imageanchor="1" style="margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"><img alt="Vanilla slice" border="0" data-original-height="605" data-original-width="806" height="240" src=/assets/2019/01/2_20190119_025247040_ios.jpg title="" width="320"></a> Yum! <a href=/assets/2019/01/20190124_061102848_ios.jpg imageanchor="1" style="margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"><img alt="French monopoly game board" border="0" data-original-height="907" data-original-width="1210" height="239" src=/assets/2019/01/2_20190124_061102848_ios.jpg title="" width="320"></a> French Monopoly - Relying on my niece to translate I’m finishing off the mini-break with the Australia Day long weekend. Caught up with the visiting rellies one last time (before they flew home) for morning tea/lunch/kicking the footy in the park (how Aussie is that!) following by dinner with my folks. A really nice day!